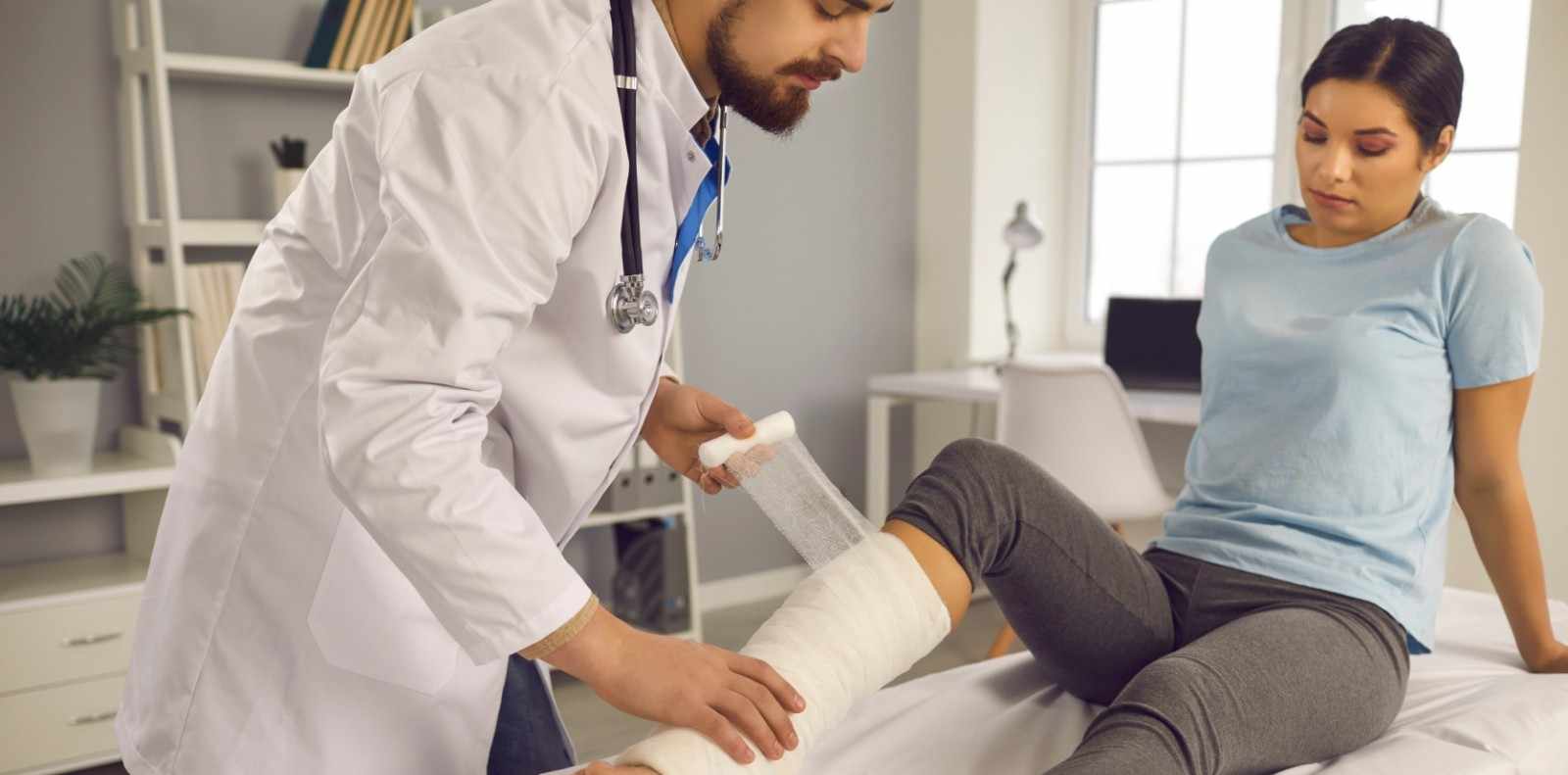
Pediatric orthopedics focuses on diagnosing and treating musculoskeletal conditions that affect infants, children, and teenagers. Growth plates, developing bones, and rapidly changing biomechanics make pediatric cases different from adult orthopedic problems. Early detection and treatment are crucial, because untreated concerns can affect mobility, growth, and long-term quality of life. Families often seek specialists such as the best orthopedic doctor in Aligarh to understand symptoms, explore treatment options, and ensure proper recovery as a child grows.
Common Pediatric Orthopedic Conditions
Children can develop orthopedic problems due to genetics, growth issues, sports injuries, posture, or trauma. Some of the most common conditions include:
Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip (DDH): A condition in which the hip joint doesn’t form properly, often identified in infancy. Failure to treat DDH early can result in arthritis and reduced mobility later in life.
Clubfoot: A congenital disorder where a baby’s foot is twisted inward. Treatment may include stretching, casting, or surgical correction depending on severity.
Scoliosis: A curving of the spine that typically appears during growth spurts. Monitoring and bracing can prevent progression, while severe cases may need surgical correction.
Flat Feet: While flat feet are common in young children, persistent pain or balance issues may require evaluation by an orthopedic specialist.
Growth Plate Injuries: Because children’s bones contain soft cartilage growth plates, fractures here need careful treatment to avoid deformities and uneven limb length.
Sports-Related Injuries in Children and Teens
With more children participating in competitive sports, overuse injuries are increasingly common. Adolescents face particular risk because their bones grow faster than muscles and tendons. Common issues include:
Osgood–Schlatter Disease: Knee pain caused by inflammation of the tendon connected to the tibia during rapid growth.
Little League Elbow or Shoulder: Overuse injuries linked to repetitive throwing motions in baseball and other overhead sports.
Stress Fractures: Small cracks in bones caused by repetitive impact rather than sudden trauma.
Addressing these injuries requires early intervention, proper training techniques, and sometimes physical therapy. Parents should consult specialists at centers such as Renuka Hospital Aligarh if symptoms persist.
Diagnostic Approaches in Pediatric Orthopedics
Children require different diagnostic strategies than adults. Pediatric orthopedic doctors use physical exams, gait analysis, X-rays, ultrasound, and MRI scans to examine bone structure and movement. In very young children, imaging may focus on growth plates and bone alignment to avoid long-term complications. A careful medical history and observation of developmental milestones also play a large role in evaluation.
Treatment Options: Conservative vs. Surgical
Conservative care is always the first option for mild to moderate pediatric orthopedic conditions. Methods may include:
Splints, braces, or casts
Stretching exercises and physical therapy
Orthotic shoe inserts
Activity modification for sports-related injuries
Surgery is recommended only if non-invasive treatments fail or if a severe deformity is present. Minimally invasive techniques and advanced implants have significantly improved recovery outcomes in young patients. As children heal faster than adults, timely procedures lead to excellent long-term results.
The Importance of Early Intervention
Early diagnosis can prevent lifelong disability. Pediatric orthopedic conditions often worsen silently because a child may not recognize or communicate pain effectively. Parents should look for warning signs such as:
Uneven walking or limping
Frequent tripping
Visible curvature of the spine
Chronic joint pain
Deformity in limbs or feet
Regular pediatric checkups, school screening programs, and sports assessments help identify problems early.
Rehabilitation and Long-Term Care
Recovery for children often includes physical therapy to build strength and improve movement patterns. Rehabilitation may emphasize:
Balance and coordination exercises
Stretching routines
Sport-specific training techniques
Post-surgical strengthening
Educating families and young patients is essential. Good posture, appropriate footwear, warm-up habits, and conditioning exercises reduce the risk of reinjury.
Advances in Pediatric Orthopedic Treatments
Modern facilities use advanced diagnostics, motion analysis, and minimally invasive surgery for precise care. Innovations in biomaterials and growth-friendly implants give children safer and more effective options. Organizations working in joint replacement india have contributed significantly to research and improved techniques in pediatric mobility care.
Final Thoughts
Pediatric orthopedic conditions are highly treatable when addressed early and managed by trained specialists. Understanding symptoms, seeking professional evaluation, and following through with treatment allow children and teenagers to return to normal activity, remain confident, and continue healthy physical development. Parents, coaches, and caregivers should stay alert to changes in posture, walking patterns, and pain complaints to ensure the best outcome for young patients.




Write a comment ...